$2.4B lost in 2025 H1 crypto hacks — exchanges and DeFi hit hardest: report

In the first half of 2025, the blockchain industry suffered over $2.37 billion in losses due to security incidents, with the DeFi sector hit the hardest. Scams targeting individual users have also proliferated, with AI enabling increasingly sophisticated schemes.
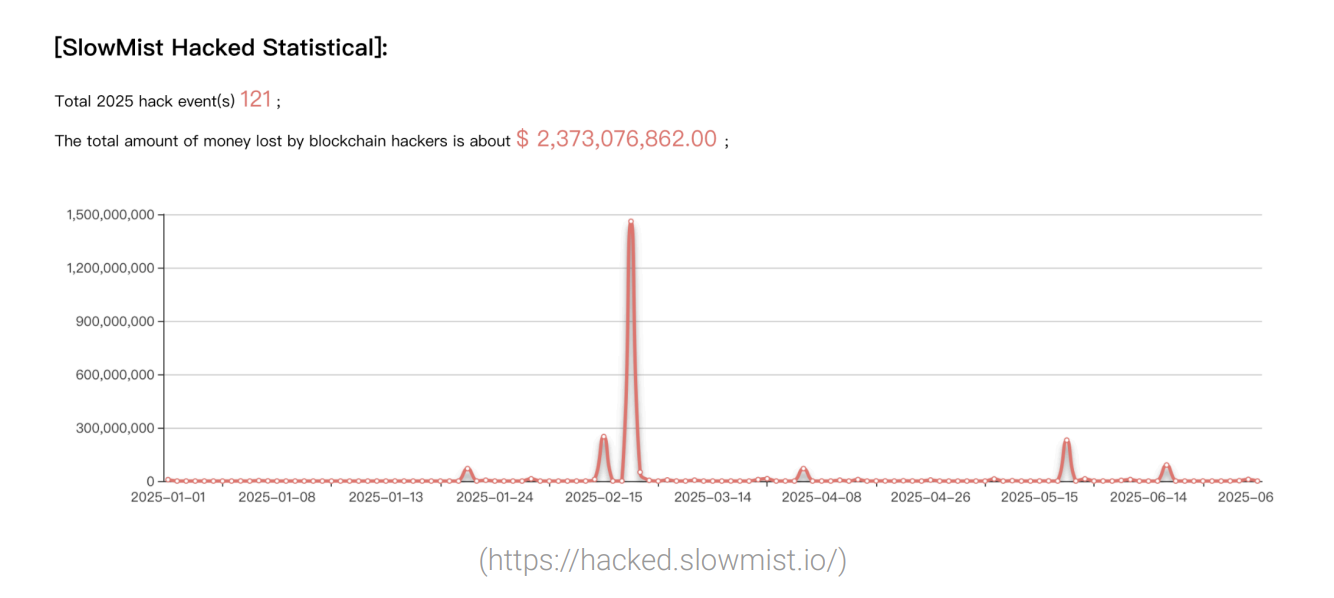
According to SlowMist’s mid-year “Blockchain Security and AML Report,” the blockchain industry saw approximately $2.37 billion in losses across 121 security incidents in the first half of 2025. This represents an almost 66% increase in financial losses compared to the same period in 2024, despite a decline in the number of incidents.
DeFi continues to be the most targeted sector, accounting for 76.03% of all incidents and approximately $470 million in losses. However, CEX platforms experienced $1.883 billion in losses from just 11 incidents, indicating high-value targets for attackers.
Account compromises were the leading cause of security incidents, followed by smart contract vulnerabilities.
Beyond direct attacks on projects, SlowMist’s report highlighted several fraud tactics targeting individual users that have characterized the first half of 2025:
Phishing Using EIP-7702
Attackers are exploiting new features of the EIP-7702 contract delegation mechanism that was introduced with Ethereum’s Pectra upgrade. On May 24, a user lost $146,551 after falling victim to a phishing attack that misused MetaMask’s EIP-7702 delegation feature. The scam, carried out by the Inferno Drainer group, tricked the user into authorizing a legitimate-looking contract, which then exploited bulk token approvals to drain funds.
Deepfakes
The rapid advancement of generative AI has ushered in a new wave of “trust-based scams.” In early 2025, a fake Zoom meeting using deepfakes led to the theft of all crypto assets from Mehdi Farooq, a partner at Hypersphere Ventures, after attackers impersonated known contacts and tricked him into downloading malware. Other high-profile cases include AI-generated videos of Elon Musk and Singapore officials promoting fake investment schemes.
Telegram Fake Safeguard Scams
These scams trick users into executing malicious code from their clipboard. Victims were lured through fake X accounts impersonating crypto influencers, then redirected to Telegram groups where “Tap to verify” links activated trojan-laced PowerShell commands. These attacks led to full device compromise, allowing remote access tools steal wallet files, private keys, and even control Telegram accounts across both Windows and macOS systems.
Malicious Browser Extensions
Disguised as “Web3 security tools” or exploiting automatic update mechanisms, these fake extensions hijack download links to install malicious software and steal mnemonic phrases, private keys, or login credentials. One high-profile case involved the “Osiris” extension, where attackers hijacked a legitimate developer’s Chrome Web Store account through a phishing-based OAuth exploit, pushing a stealthy malicious update to over 2.6 million users.
LinkedIn Recruitment Phishing
In 2025, LinkedIn-based phishing surged as attackers posed as blockchain startups to lure engineers into downloading malware disguised as technical tests. Scammers shared professional-looking project briefs and design documents, eventually sending victims to repositories containing heavily encrypted malicious payloads. Once executed, these backdoors steal host information, credentials, SSH private keys, and system Keychain data.
Social Engineering Attacks
Social engineering scams surged in early 2025, with the most high-profile case involving Coinbase. In this incident, attackers bribed overseas customer support staff to leak user data, then impersonated Coinbase reps using spoofed phone numbers and phishing messages to lure victims into transferring funds to wallets controlled by scammers. According to SlowMist, such coordinated attacks resulted in over $100 million in total user losses.
Backdoor Supply Chain Attacks via Low-Cost AI Tools
Developers seeking “unlimited access to advanced AI models” via unofficial channels risk installing malicious npm packages that deeply tamper with local applications. SlowMist flagged a case where a startup lost hundreds of thousands due to malicious code generated by such a tool, which installed backdoors via npm packages. Over 4,200 developers, mostly on macOS, were affected, allowing attackers remote control and credential theft.
Unrestricted Large Language Models
SlowMist’s report highlights several LLMs that have been “jailbroken” to bypass the ethical restrictions of their original versions. WormGPT specializes in generating malware-related content and phishing emails, while FraudGPT can produce fake crypto project materials and clones phishing pages. DarkBERT, trained on dark web data, enables highly targeted social engineering campaigns. GhostGPT can create deepfake scams impersonating exchange execs, among other malicious uses.






